| Veterinary
Histology UFF Department of Morphology - Biomedic Institute LaBEc - Laboratory of Cellular and Extracellular Biomorphology |
|||
Veterinary
Histology Atlas |
|||
Nervous
Tissue |
|
General Characteristics •
Originates from the neuroectoderm |
|
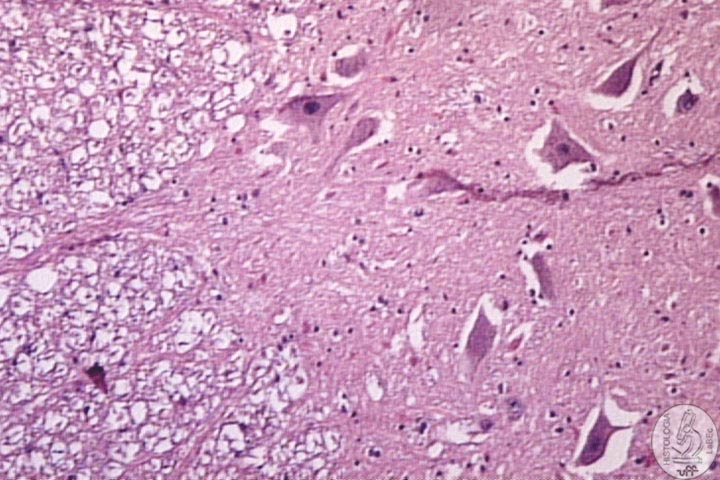
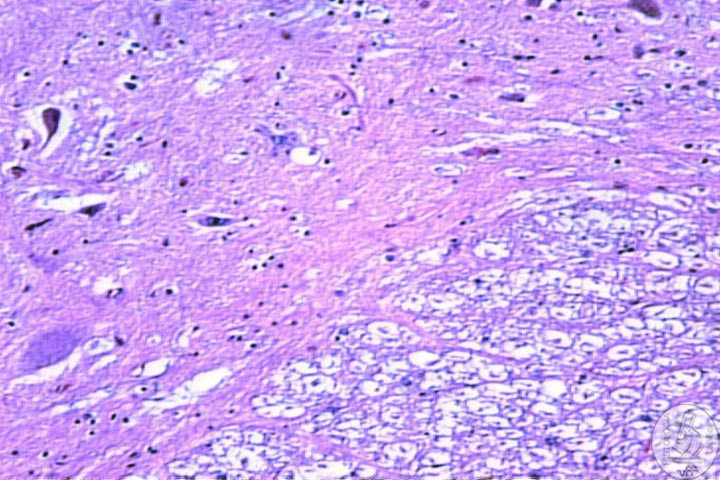
| Gray
matter • Cell bodies of neurons • Glial cells • Neuron extensions |
|
| White
matter • Neuron extensions(myelinated) • Glial cells |
|
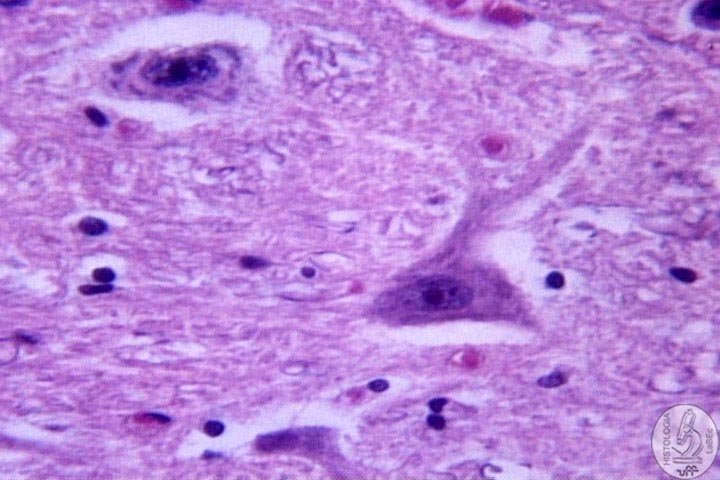
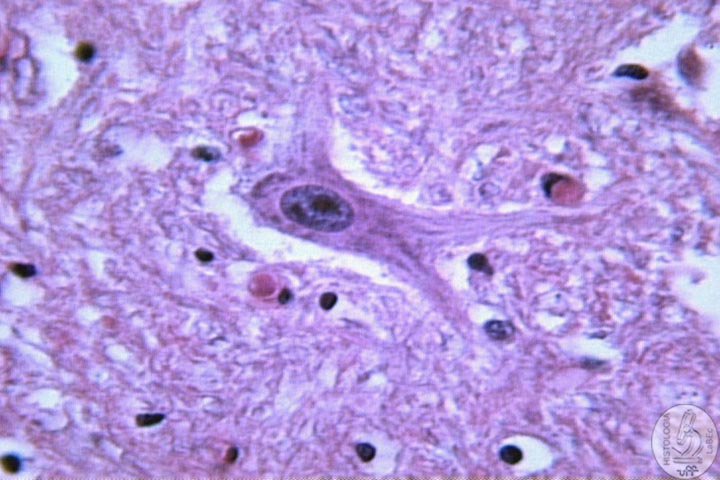
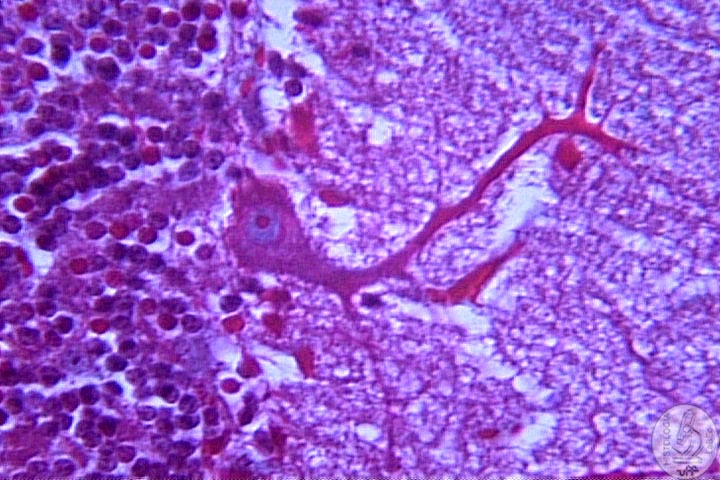
Components I - Neurons Function: Reception, integration, conduction and transmission of nerve impulses. Constitution |
|
| I
- Cell Body • Central portion of the cell |
|
| • Presents Nissl bodies (Are cisterns of RER and polyribosomes) | |
II
- Dendrites |
|
| III
- Axon • Single extension • Conduction of impulses • Transmit information from the neuron to other cells • Can be myelinic or amyelinic • Possesses many terminal buttons(region of synapses) |
|
Classification According
to morphology: According
to function: |
|
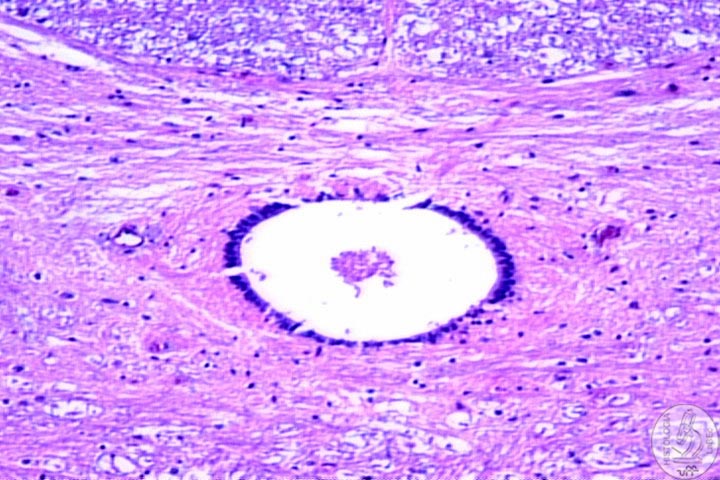
II - Glial Cell Function Characteristics Representatives: I
- Astrocytes II - Oligodendrocytes: Responsible for the production of the myelin sheath in the CNS III - Microglia: Act as phagocytes in the elimination of residues and damaged structures |
|
| IV
- Ependymal • Modified epithelial cells • Line the encephalic ventricles and the central canal of the spine |
|
| V
- Schwann Cell • Responsible for the production of the myelin sheath in the PNS |
|
| Synapse and Transmission of Nerve Impulses Synapse:
Sites where nerve impulses are transmitted from the presynaptic
to the postsynaptic cell. Can be electrical or chemical Chemical:
Use
of neurotransmitters to diffuse themselves to the receptors in
the postsynaptic membrane |
|
| Types
of synaptic contact Neurotransmitters Myelin
Sheath |
|