| Veterinary
Histology UFF Department of Morphology - Biomedic Institute LaBEc - Laboratory of Cellular and Extracellular Biomorphology |
|||
Veterinary
Histology Atlas |
|||
Urinary
System |
|||||||||||||||
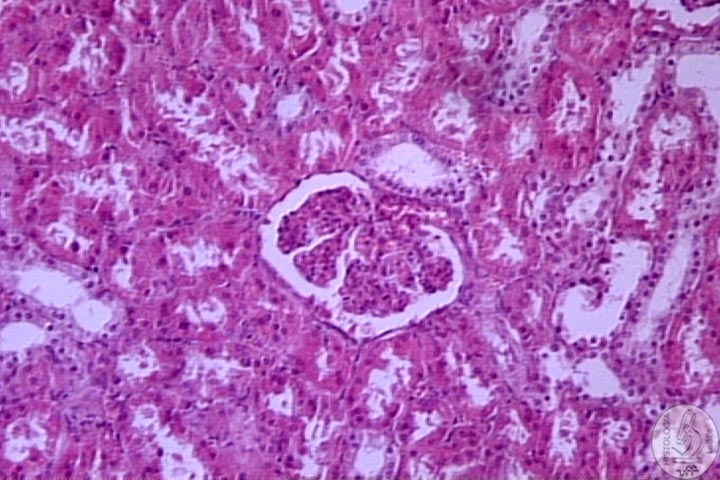
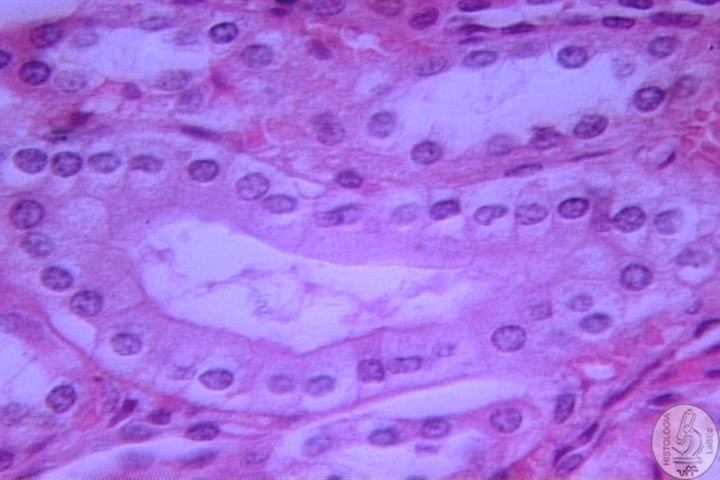
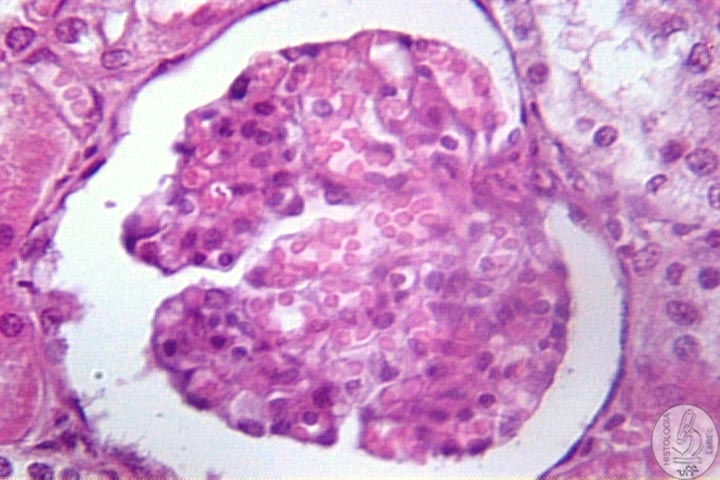
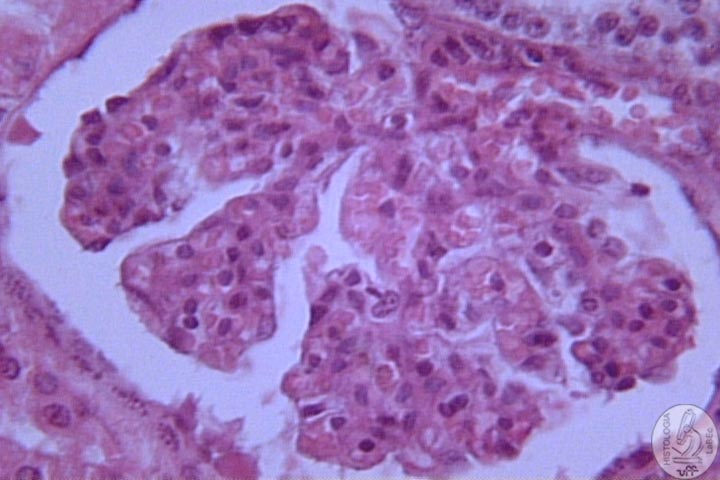
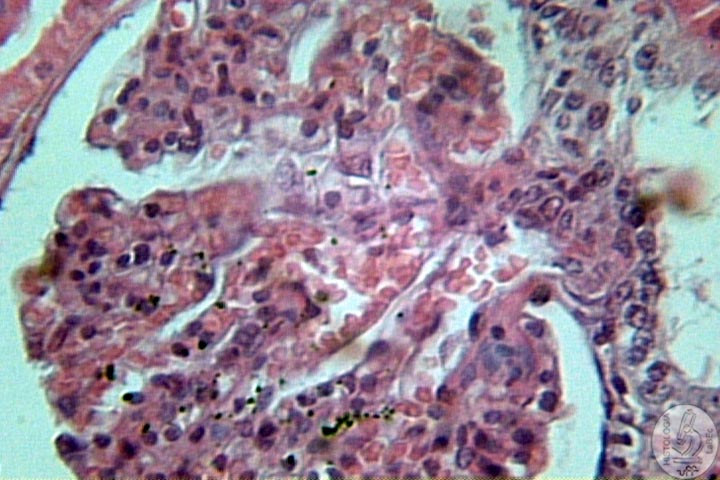
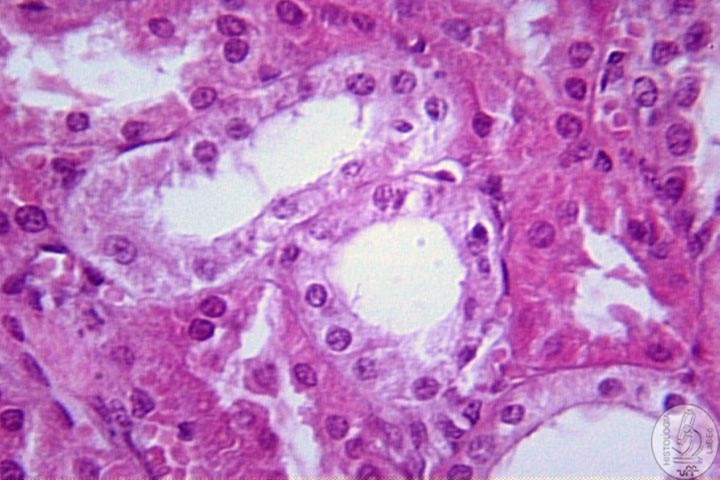
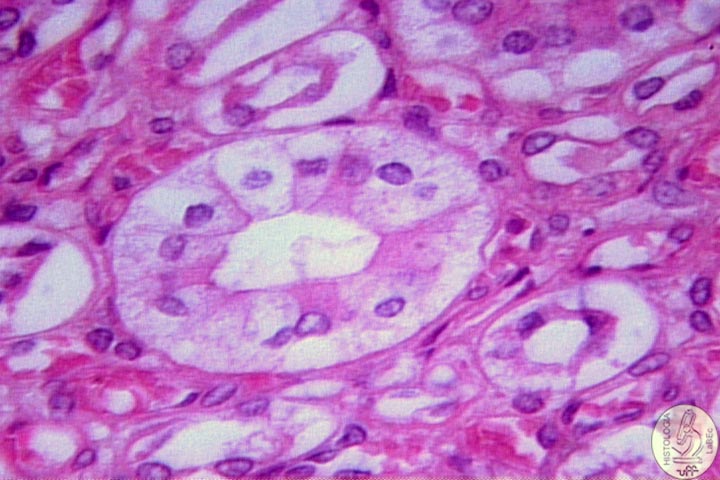
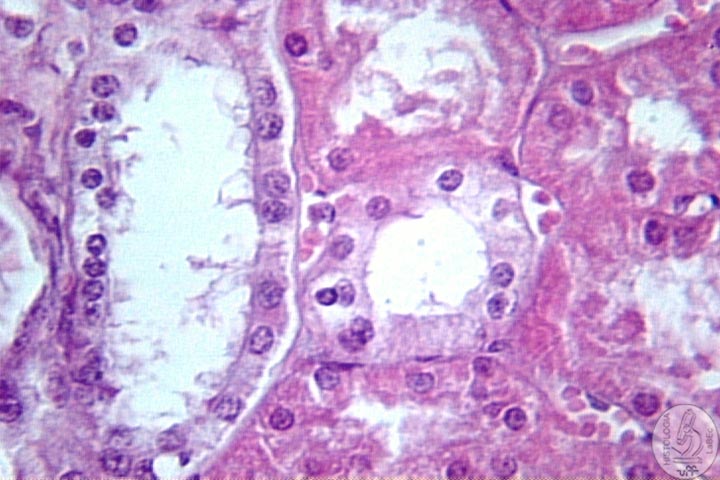
| Functions Constitution Kidney
Néfron
|
|||||||||||||||
| Bladder Mucosa Muscularis Adventitia or Serosa: In the upper portion of the bladder there is a serosa, the rest is adventitia
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ureter • Present the same basic structures as the bladder, less thick • Has a valve that prevents the reflux of urine |
|||||||||||||||
| Urethra • Tube that takes the urine from the bladder to the outside |
|||||||||||||||
| Male
Urethra Prostatic Membranous Penile
or Cavernous Female
Urethra
|