| Veterinary
Histology UFF Department of Morphology - Biomedic Institute LaBEc - Laboratory of Cellular and Extracellular Biomorphology |
|||
Veterinary
Histology Atlas |
|||
Blood |
|
General
Characteristics Study Methods Quantitative Macrohematocrit:
Analyzes the % of the fractions of blood elements
after macrocentrifugation. Microhematocrit: Similar to macrohematocrit however microcentrifugation is used instead Qualitative Blood
Smear: Erythrocytes are observed, to visualize the
leukocytes, dyes are used |
|
Components Plasma Blood Cells Hematids
or Erythrocytes |
|
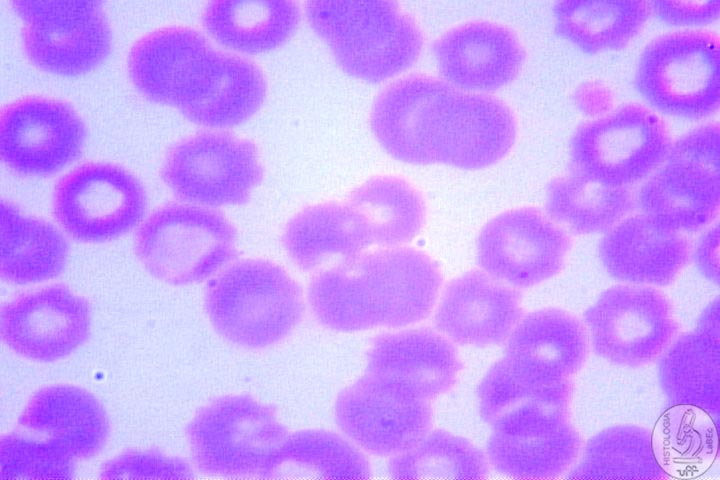
•
Disk-like shape |
|
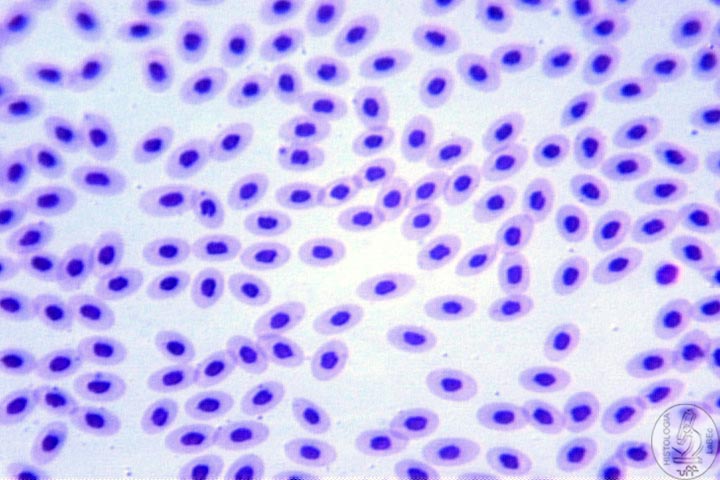
• Erythrocytes in birds are nucleated |
|
| •
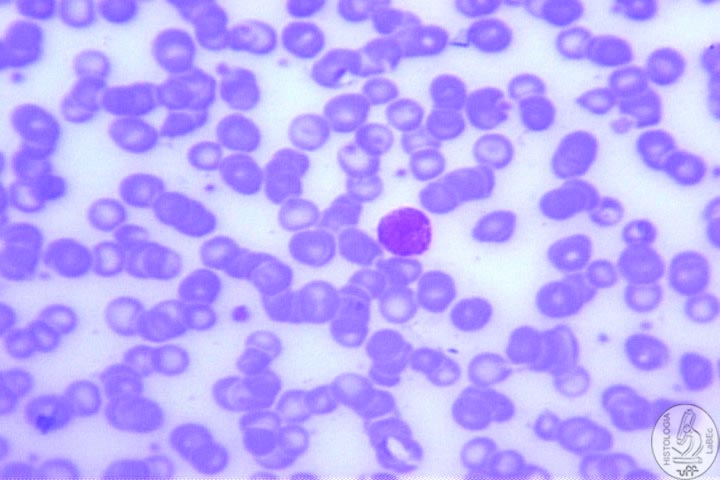
Originate from the erythroblast in the red bone marrow • Store hemoglobin(carry oxygen and carbon dioxide) • Measure 7.2 to 8.0 micrometers in diameter • Shape given by the amount of hemoglobin • Erythrocytes need to be perfect in size, morphologically and physiologically |
|
| Morphological Abnormalities: Poikilocytosis:
Erythrocytes with Abnormal Shape(Ex: Sickle-cell erythrocytes) Anisocytosis:
Difference in the size of erythrocytes |
|
| Reticulocyte • Erythrocyte soon after loss of its nucleus • Contain many ribosomes and therefore can present an altered coloring |
|
Leukocytes Granulocytes: Possess a specific granulation |
|
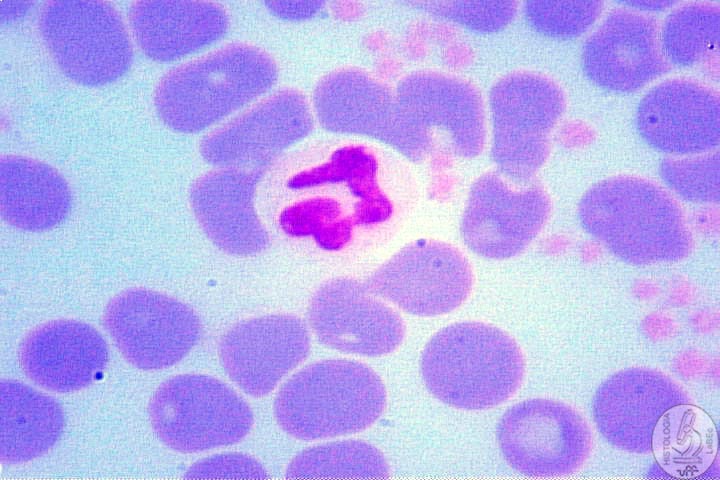
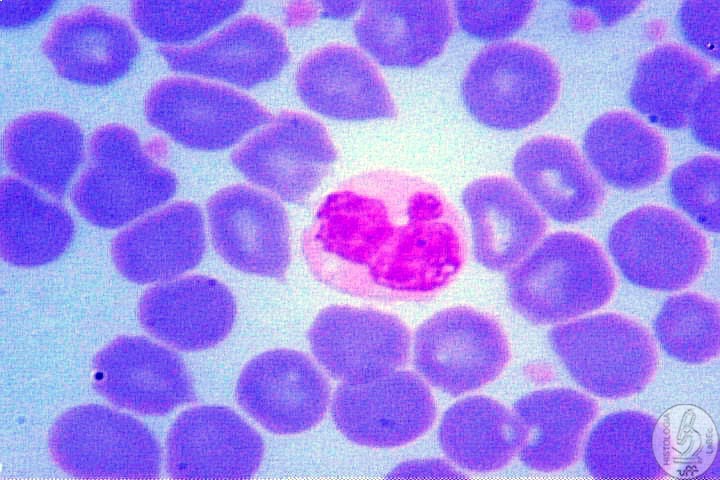
| Neutrophils • Granules have no affinity with any type of Dye(Neutral) - Specific: lactoferrin and lysozyme - Non-specific: lysosomes • Nucleus nicely segmented, generally 3 segmentations - 4 or more segmentations: hipersegmented(old) - Less than 3 segmentations: young, still in formation, can present baton-shaped nucleus • Phagocytosis of Bacteria |
|
| Eosinophil • Granules have affinity with eosin: - Internum - Externum(Synthesis of Enzymes) • Bilobulated nucleus • Related to Allergic Process(possess IgE receptors) • Combats Parasites |
|
| Basophil • Granules have affinity with hematoxylin • Great amount of granules - Histamine - ECF-A - Heparin • Nucleus in the shape of a convoluted “S”(contracted over itself) • Related to Allergic Process(possess IgE receptors) |
|
| Agranulocytes: Possess only non-specific granulations(lysosomes): | |
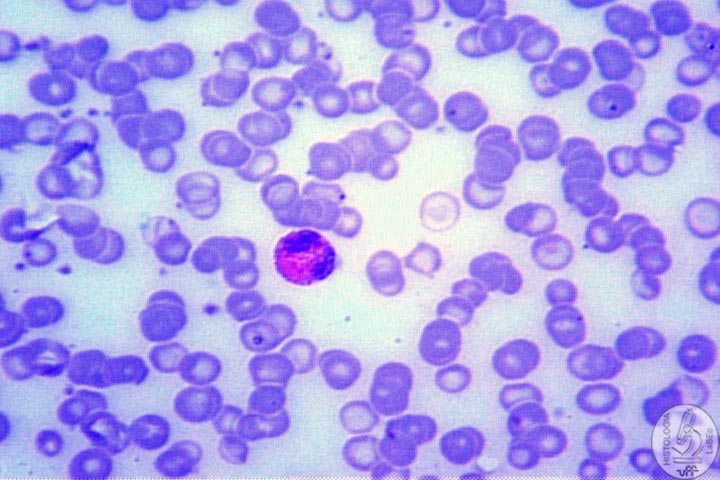
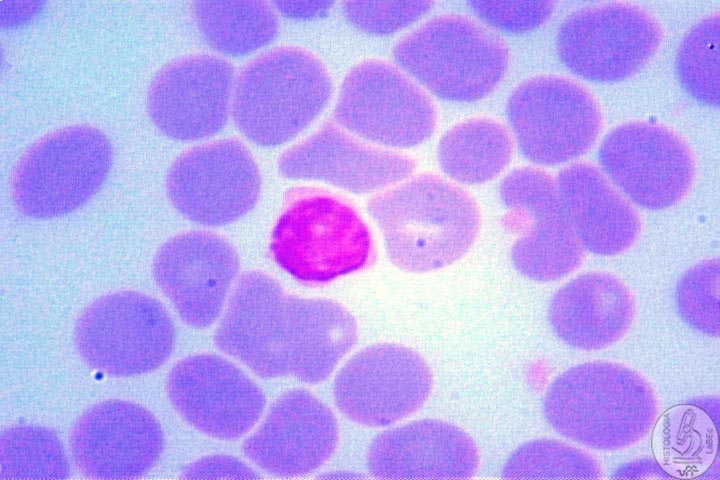
| Monocyte • Large Cells • Chromatin mostly pale • Acidophilic(many ribosomes) • Irregular nucleus • Originates macrophages |
|
| Lymphocyte • Great Nucleus/Cytoplasm Relation • Spherical nucleus • Dense Chromatin |
|