| Veterinary
Histology UFF Department of Morphology - Biomedic Institute LaBEc - Laboratory of Cellular and Extracellular Biomorphology |
|||
Veterinary
Histology Atlas |
|||
Female
Reproductive System |
|||
| Functions Components Internal Reproductive Organs
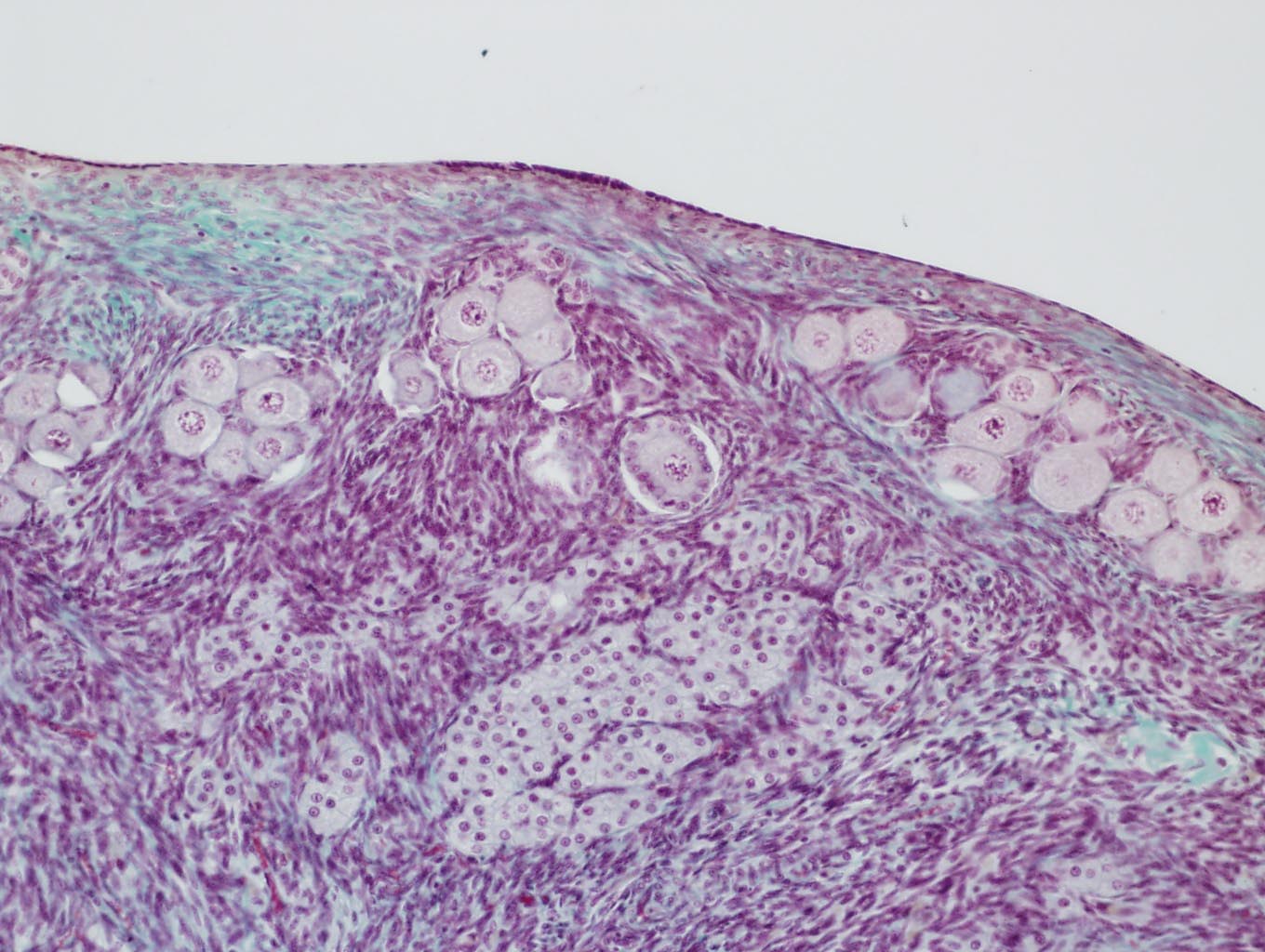
Ovaries
Cortex |
|||
| Primordial
Primary Secondary
|
|||
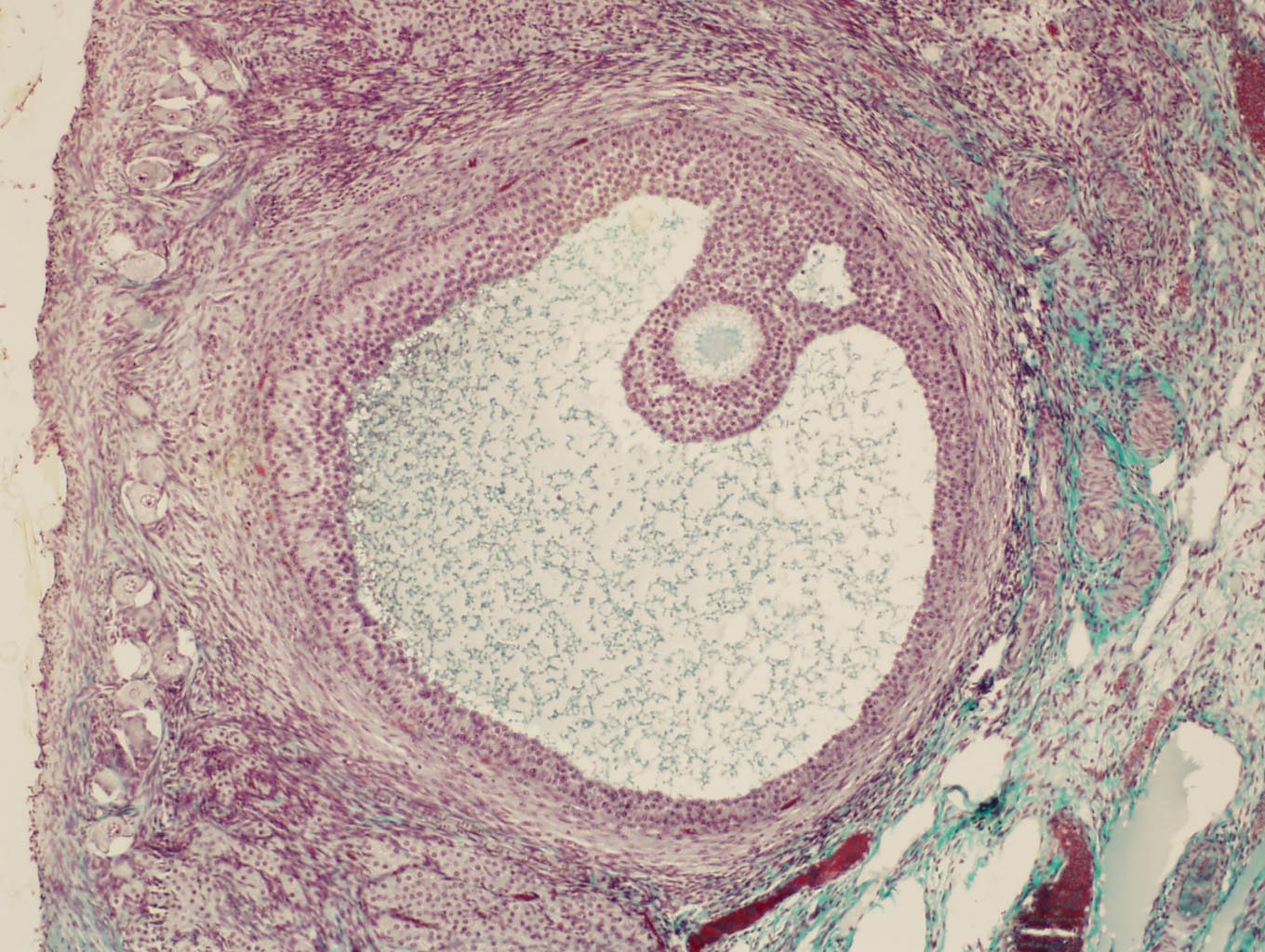
| Mature (Graafian) | |||
| |
•
Much greater dimensions |
||
|
Corpus Luteum or Yellow Body • Found in activity • Cells from the wall of the mature follicles, after the ovulation (expulsion of oocyte II) • Possess granulosa lutein cells (Produce progesterone and estrogens) • Theca lutein Cells (Produce Progesterone) Corpus
albicans |
|||
| Medulla Formation
of ovocyte |
|||
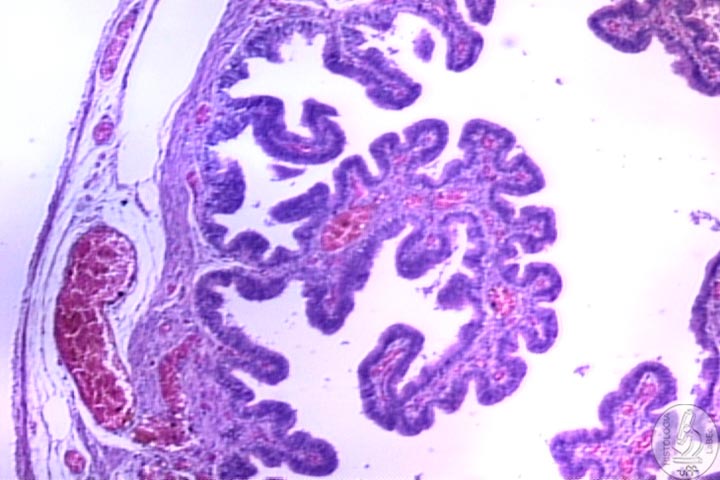
Oviduct
(uterine tubes) Infundibulum Ampulla Isthmus Intramural
Region Has three layers: |
|||
| |
Mucosa Muscularis Serosa |
||
| Uterus Presents three regions: Corpus
and Fundus |
|||
| Endometrium Myometrium Adventitia
or Serosa
|
|||
| |
Dispersed uterine glands in the lamina propria of uterine mucosa. |
||
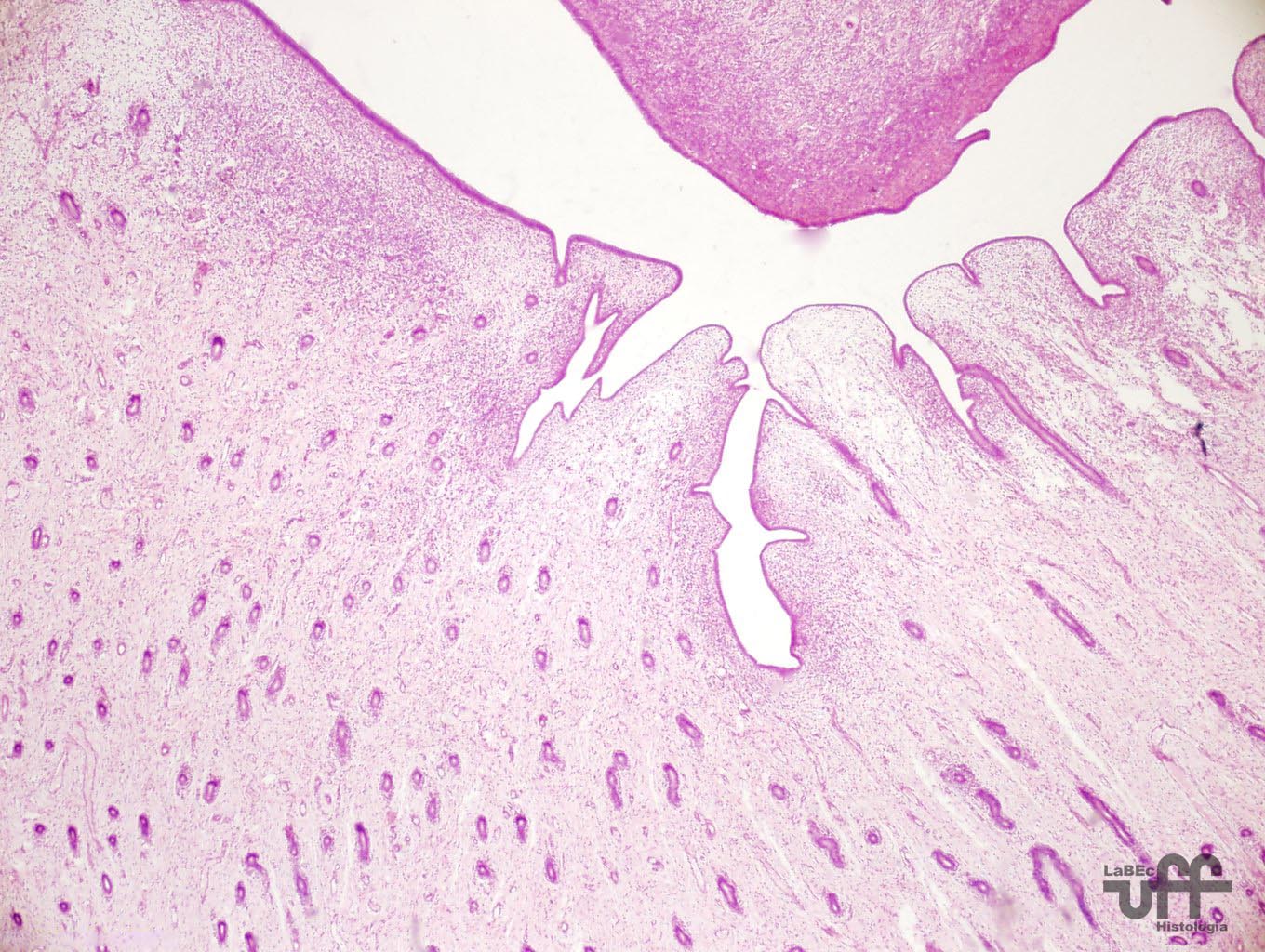
| Cervix
• Opens inside the vagina • Has cervical glands in the mucosa |
|||
| Vagina • Lined by Non-keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium. • The vaginal mucosa is normally non-glandular |
|||
| Mammary
Glands • Formed by 15 to 25 lobes • Each one is an independent gland (compound tubuloalveolar) • Involved by a dense connective tissue and adipose tissue • Divided in lobules by a loose connective tissue • Present: |
|||
| Lactiferous
ducts • Present a stratified squamous epithelium • Closer to the secreting unit, the epithelium becomes simple cubical • In the walls of the ducts there are smooth muscle fibers • The lactiferous ducts dilate, forming lactiferous sinus |
|||
| Tubuloalveolar
secreting portions • Final portions are dilated forming alveoli • Present a simple cubical epithelium • Myoepithelial cells are found involving these |
|||
|
The nipple presents: • Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium • Below there is dense connective tissue with smooth muscle fibers • The skin that surrounds the nipple constitutes the areola |
|||