| Veterinary
Histology UFF Department of Morphology - Biomedic Institute LaBEc - Laboratory of Cellular and Extracellular Biomorphology |
|||
Veterinary
Histology Atlas |
|||
Male
Reproductive System |
||
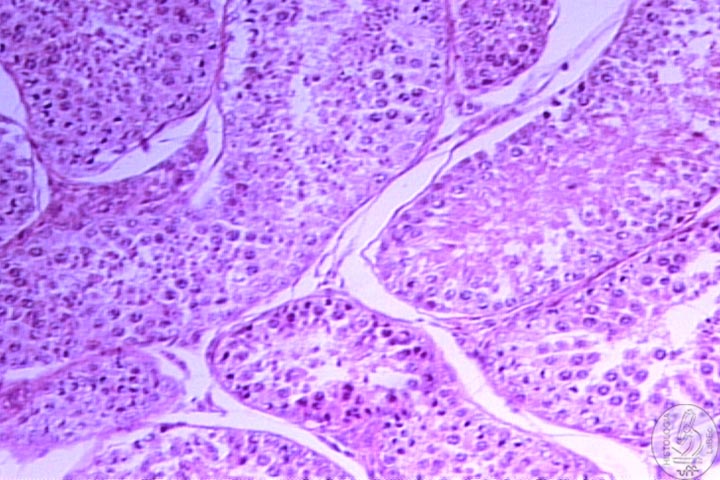
| Functions
Testicles
|
||
|
•
The seminiferous tubules are lined by seminiferous epithelium
where we find two cell lineages (seroli cells and spermatogenic
cells).
|
|
| Tunica
Albuginea lSpermatogenic
Cells
I- Spermatogonia II-
Primary Spermatocytes III-
Secondary Spermatocytes IV-
Spermatids |
||
|
Spermatogenesis: Process of the formation of spermatozoa Spermiogenesis: Transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa
|
||
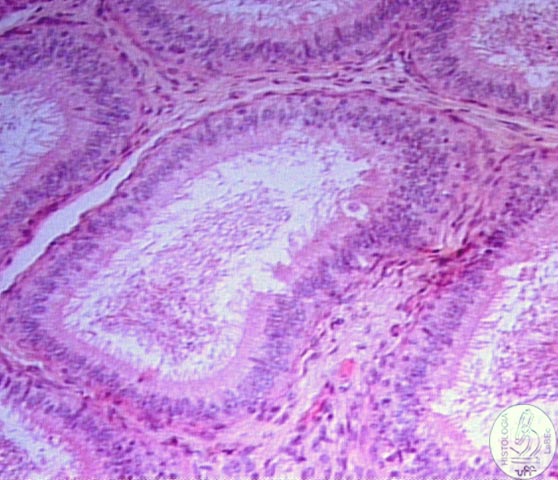
| Genital Ducts Tubuli
recti Rete
testis >> Tubuli recti and Rete testis: Connect the seminiferous tubules to the epididymis Epididymis
Efferent ductules |
||
|
|
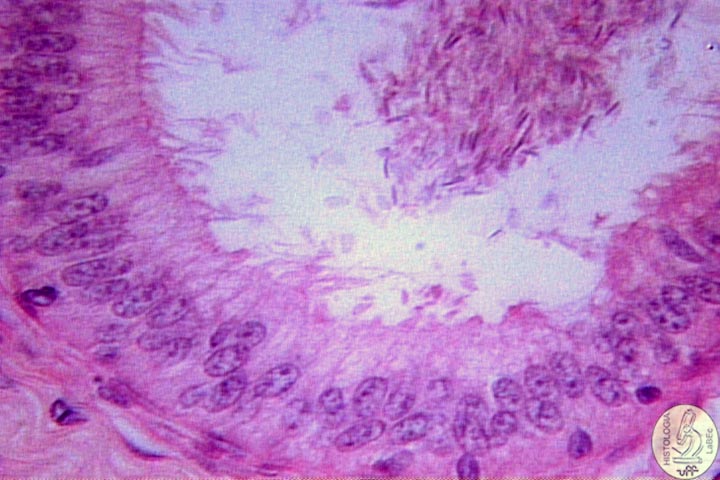
Epididymis
duct • Lined by a stereociliated pseudostratified cylindrical epithelium associated with connective tissue with smooth muscle cells • Highly contorted • During the path through the epididymis, the maturation of the spermatozoa occurs, with the absorption of cytoplasmic residues from the spermiogenesis process. The spermatozoa are stored in the tail of the epididymis until ejaculation. |
|
|
||
| Ductus
Deferens |
||
| Accessory genital glands Seminal
vesicles |
||
|
|
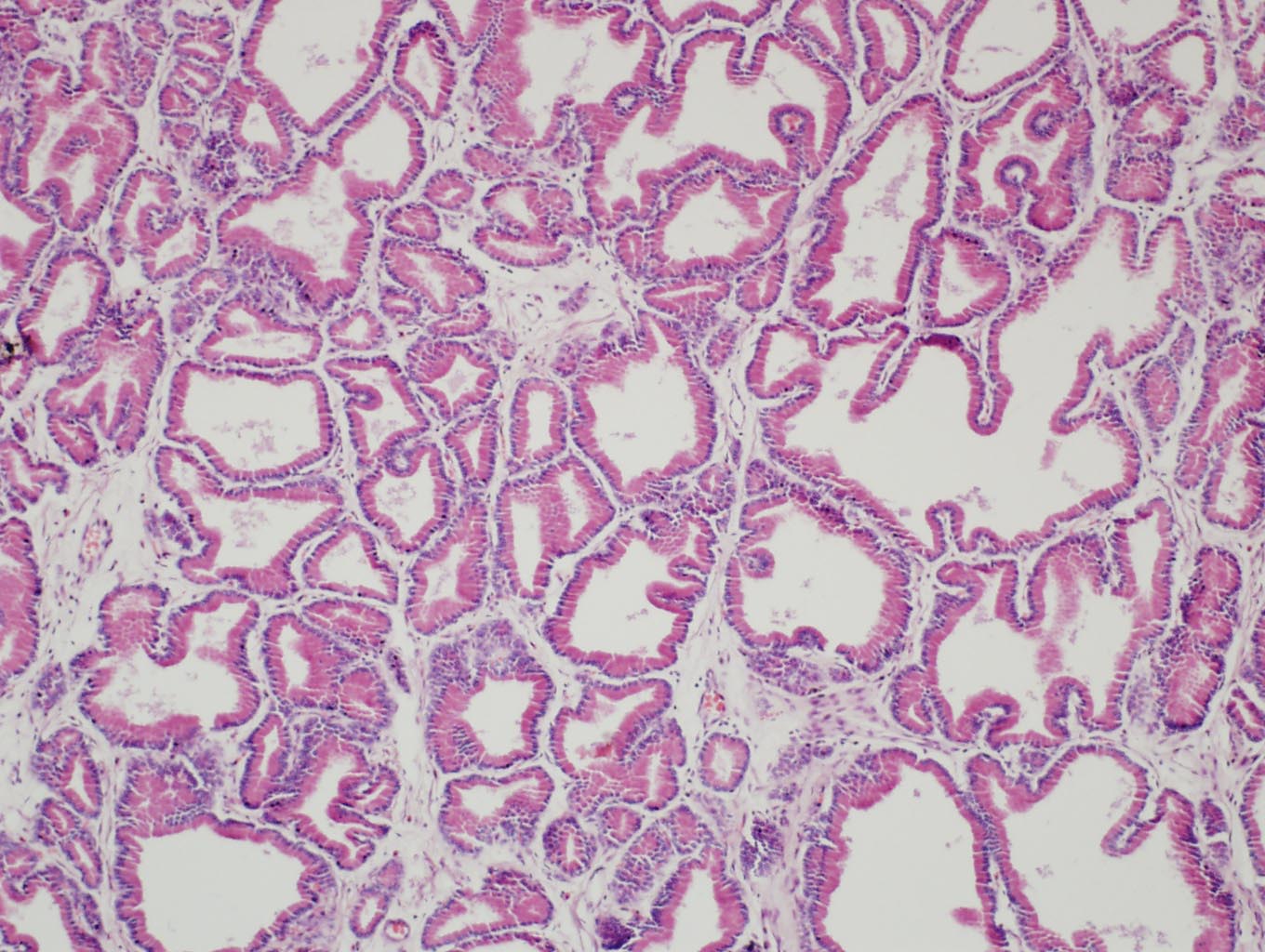
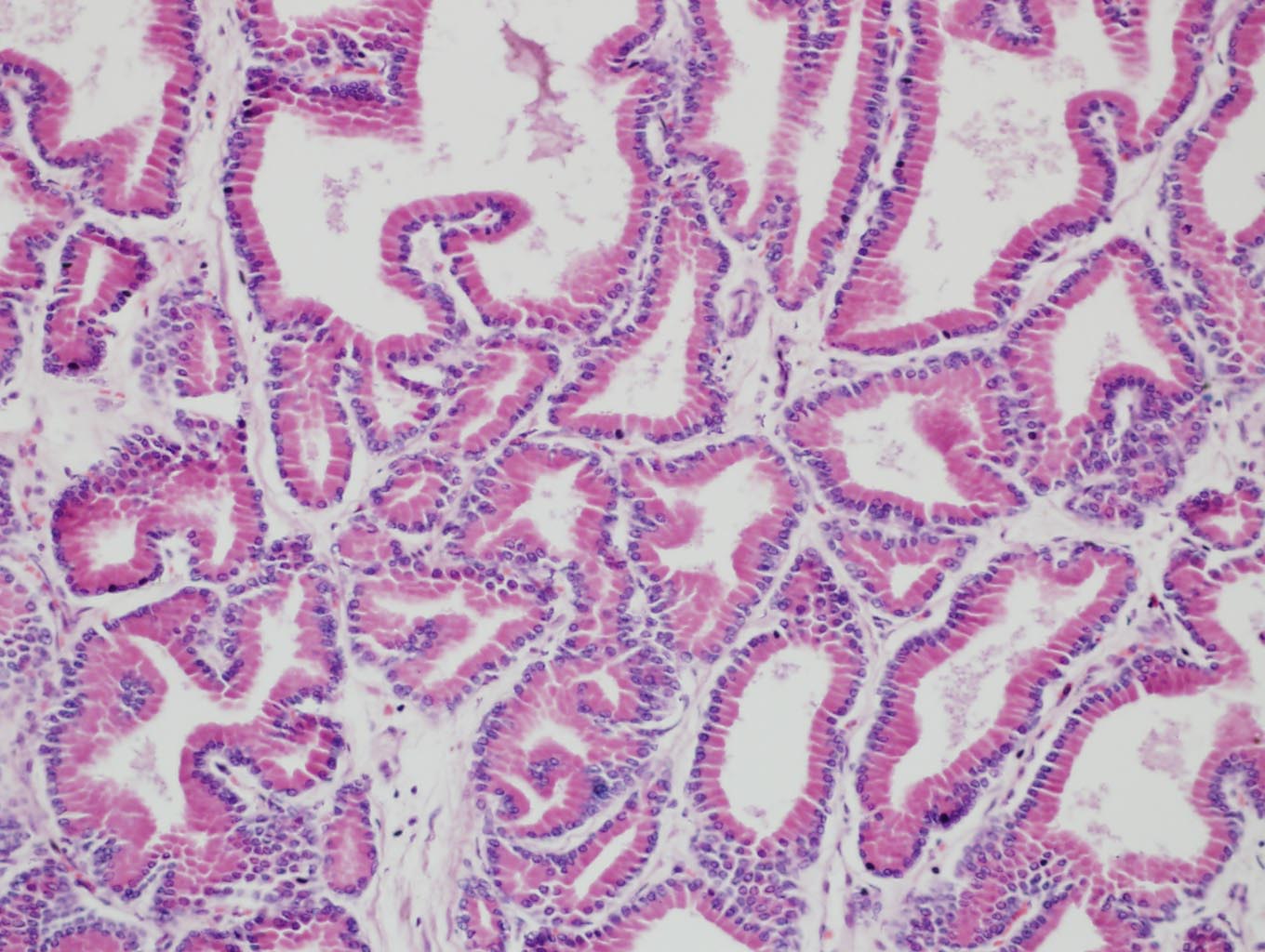
Prostate • It has a capsule of dense irregular fibroelastic connective tissue with smooth muscle cells • The parenchyma is formed by various individual tubuloalveolar glands • The mucosa with folds of the glands is lined by a variable epithelium. It can be simple cuboidal or simple columnar epithelium. In some regions, it is pseudostratified columnar epithelium. • The mucosa is supoorted on a fibroelastic connective tissue that is highly vascularised and has smooth muscle cells • Produces a white and serous fluid |
|
|
||
| Bulbourethrals |
||
Penis |
||
|
|
• Two corpora cavernosa are located dorsally |
|
|
•
Corpus cavernosum (or spongiosum) of the urethra is located ventrally • Corpus cavernosum (or spongiosum) of the urethra is lined by a variable epithelium. It can be pseudostratified columnar or stratified columnar epithelium, and in some regions stratified squamous epithelium • We find the glands of Littré (mucous secretion) throughout the urethra. |
|
|
|
||
 |
• The three corpora cavernosa are surrounded by a tunica albuginea of the penis. | |