Respiratory
System |
Basic
Mechanism
Respiration
•
Movement of the air in and out of the lungs (ventilation)
• Supplies oxygen to the cells and eliminates carbon dioxide
Division
Conducting
Portion of the Respiratory System

|
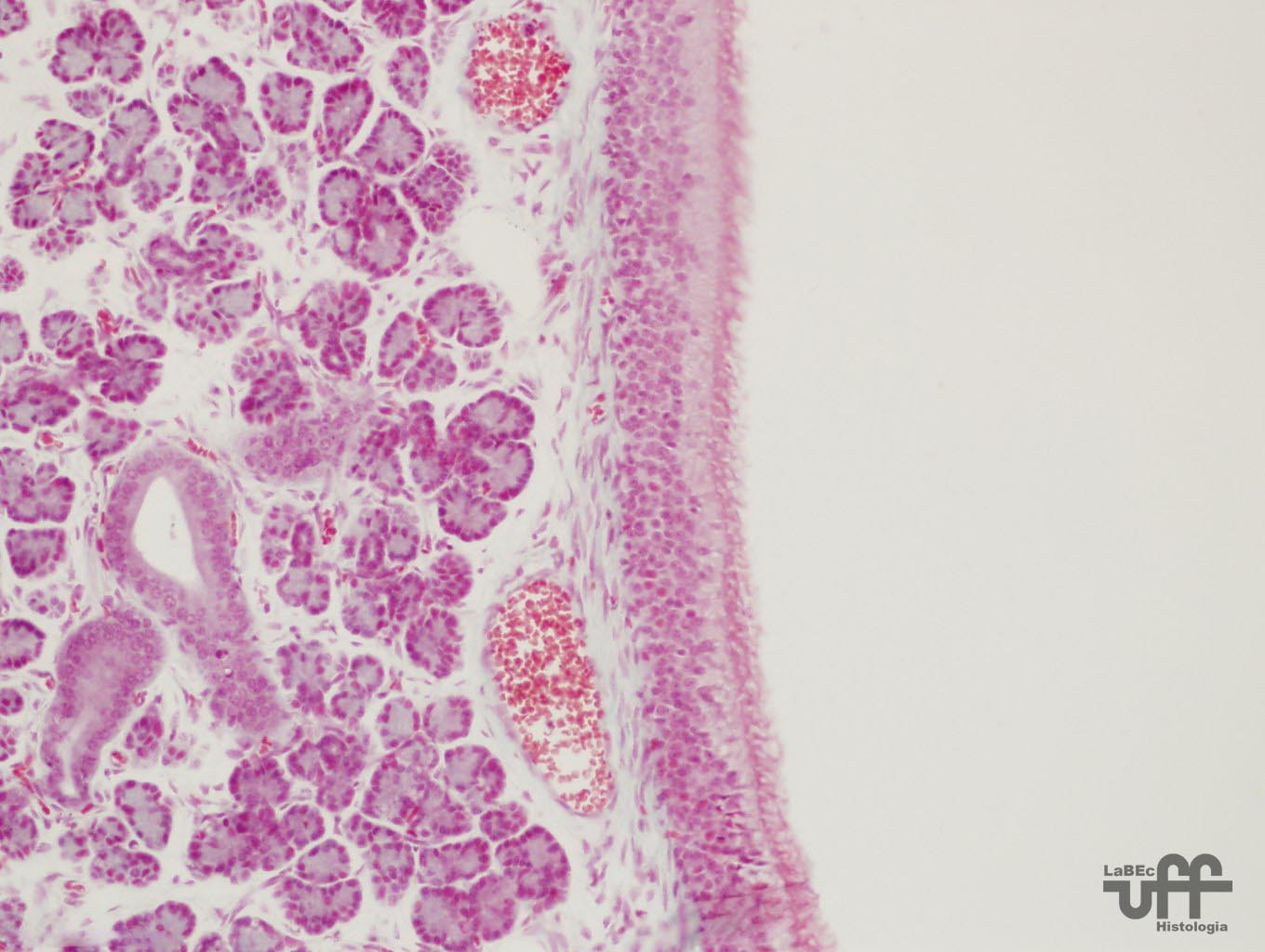
Nasal
Cavity
•
Anterior Portion or Vestibule: Covered by Skin and present
vibrissae
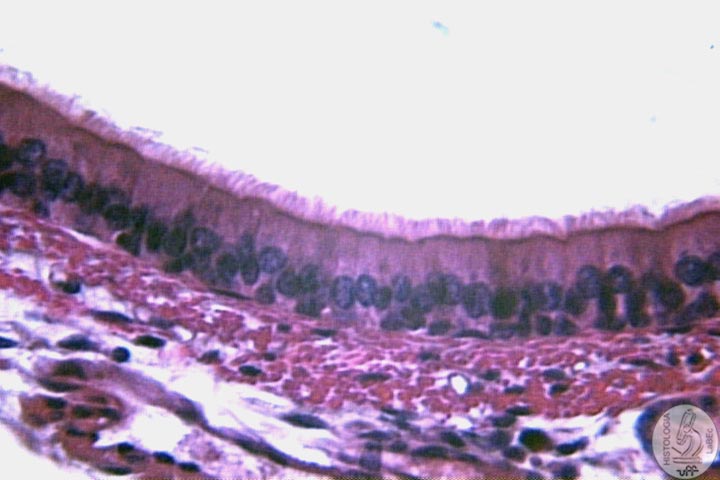
• Posterior Portion: Lined by a pseudostratified
ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
• Olfactory Region: The top of the nasal cavity
is lined by olfactory epithelium |
| 
|
The
olfactory epithelium is made up of:
•
Olfactory Cells
• Sustentacular Cells
• Basal Cells
|
|
•
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells. |
| Pharynx
Subdivided
into three regions:
• Upper Nasopharynx: Lined by pseudostratified ciliated
columnar epithelium with goblet cells
• Middle Oropharynx: Lined by Stratified non-keratinized
squamous epithelium
• Lower Laryngopharynx: Lined by Stratified non-keratinized
squamous epithelium
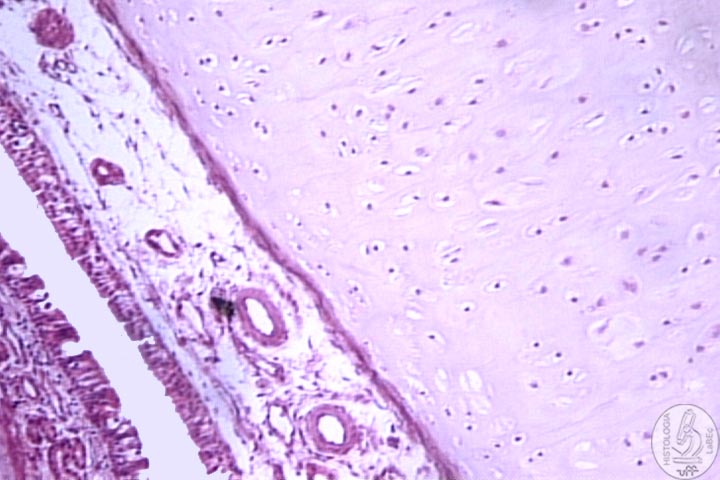
Larynx
•
Responsible for the phonation
• Lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
• Presence of the epiglottis (elastic cartilage):
Prevents
the entrance of liquids and solids into the respiratory system
during deglutition.
|
|
Trachea
•
We find 16 to 20 pieces of cartilage (hyaline) with a horse-shoe
shape
• From the inside out we find the:
Mucosa
• Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet
cells
• Lamina propria formed by loose connective tissue rich
in elastic fibers
• We find mucous and serous acinar glands
Submucosa
• Between the mucosa and the cartilage
• Presents a great amount of elastic fibers
• Presence of numerous blood vessels
Adventitia:
Loose connective tissue
|
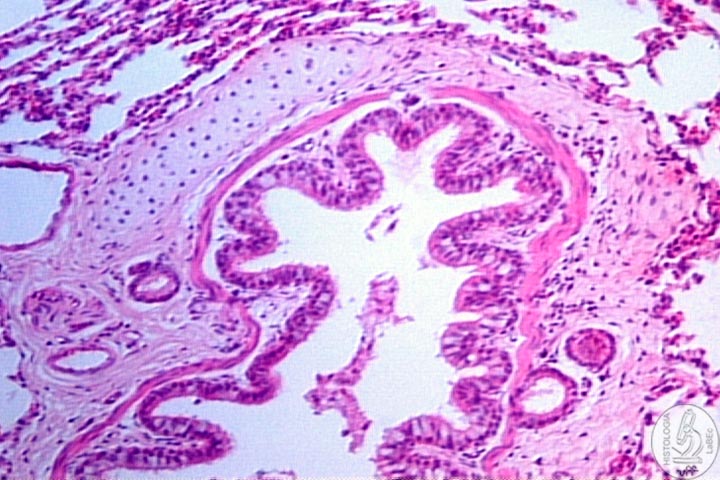
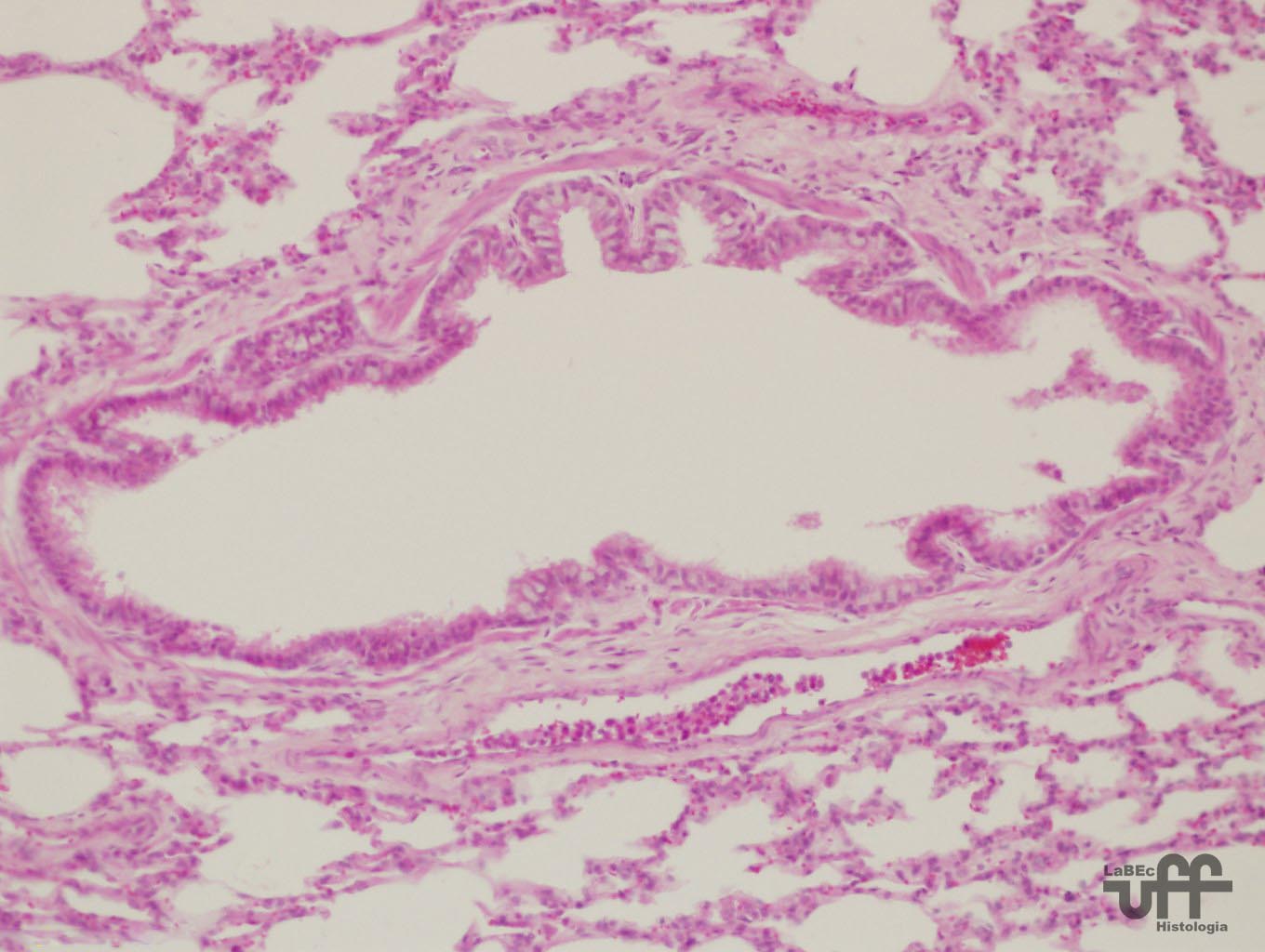
| Bronchial
Tree
Extrapulmonary
bronchi : Identical to the trachea
|
Intrapulmonary
bronchi
• The C rings are substituted by irregular plates
of cartilage
• There are two layers of smooth muscle separating
the lamina propria from the submucosa
|
|
|
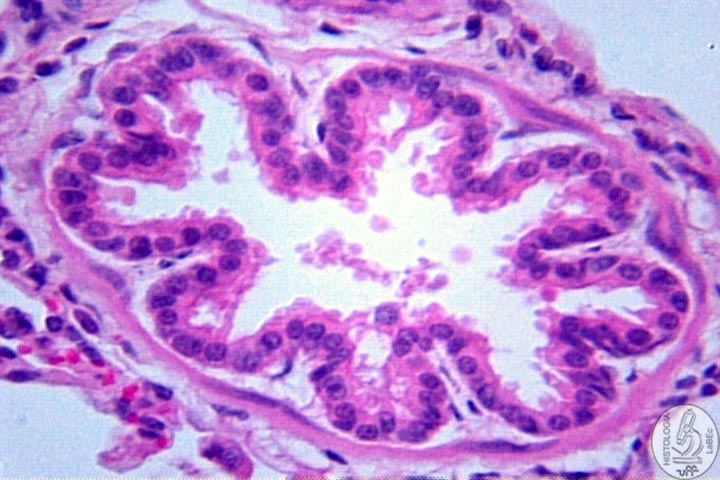
Bronchioles
Lining epithelium is variable
• Pseudostratified ciliated columnar with goblet cells
• Simple ciliated columnar with goblet cells
• Lamina propria with no glands and surrounded by layers of
smooth muscle.
Do not possess cartilage. Protect and regenerate the bronchial epithelium
|
|
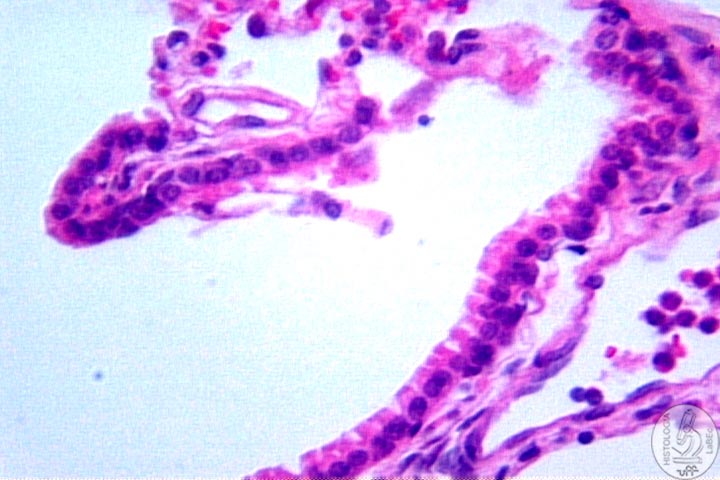
Terminal
Bronchioles
• Cubic cells with a few cilia
• Possess Clara cells(secretors)
• Lamina propria of connective tissue surrounded by smooth
muscle cells |
|
Epitélio
Bronquíolo Terminal e Respiratório
• Cubic cells with a few cilia
• Possess Clara cells (secretors)
• Lamina propria of connective tissue surrounded by smooth
muscle cells
|
|
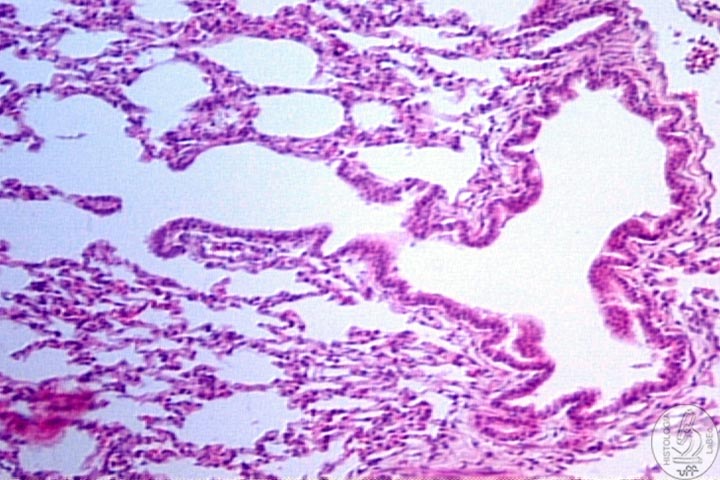
Respiratory
Portion of the Respiratory System
|
Respiratory
bronchioles
• Similar to the terminal bronchioles
• Have their walls interrupted by alveoli |
|
Epithelium
of Respiratory Bronchiole
• Simple cuboidal epithelium
|
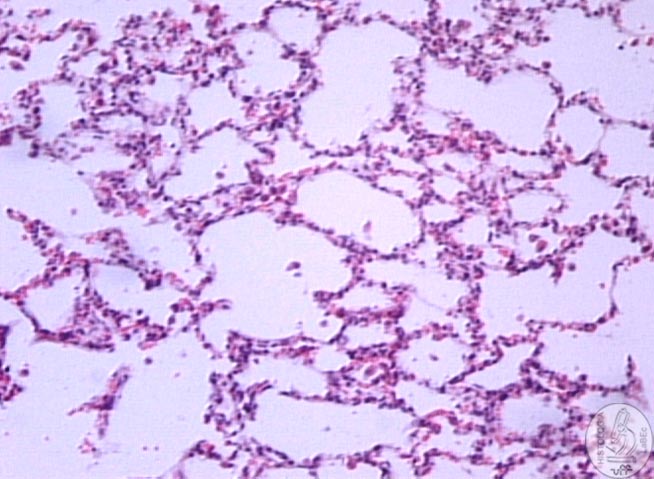
Alveolar
Ducts
• Are alveoli in linear arrangements
• End in alveolar sacs
|
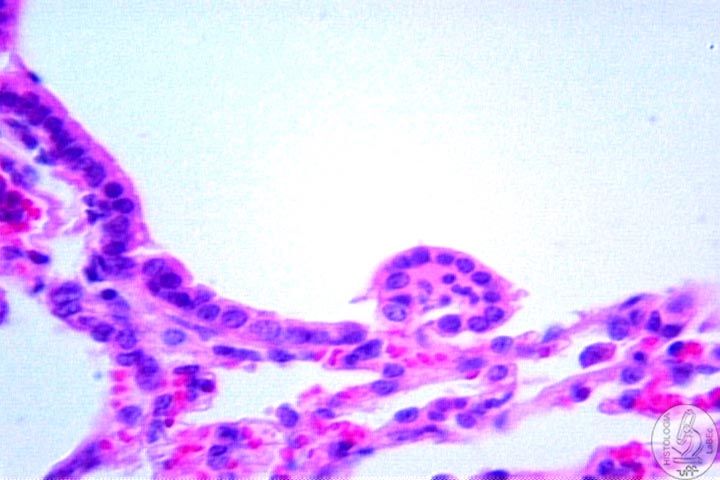
Alveoli
• Have very thin walls
• Allow the exchange of CO2 for O2
• The walls of the alveoli have:
Type
I pneumocytes: Constitute the squamous epithelium
Type
II pneumocytes:
• Cubic Cells
• Secrete pulmonary surfactant (Reduces the surface
tension and avoids the collapse of the alveolus)
Alveolar
macrophages: Dust
cells that perform phagocytosis |
|
Pleura
• Serosa membrane, Connective tissue plus Meothelium.
|
|











